Ever wondered what goes into creating a hyperbaric chamber, those special facilities that deliver oxygen therapy for a range of health conditions? Constructing these chambers is a complex process that demands intricate knowledge and attention to detail.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the vital steps involved in constructing a safe and efficient hyperbaric chamber. We’ll cover everything from understanding the basic requirements to carrying out the final safety checks. For individuals interested in building a hyperbaric chamber for their business, this is the resource.
Read on to discover the ins and outs of this fascinating process.
1. Understanding Hyperbaric Chamber Requirements
The first pivotal step is to establish the requirements of the hyperbaric chamber. Here’s what you need to consider:
Defining Purpose and Usage
The purpose and usage of a hyperbaric chamber primarily determine its design and construction. Whether the chamber is meant for medical use, providing oxygen therapy, or for deep-sea diving training will significantly influence its design specifications. According to Wound Clinic, hyperbaric chambers must be constructed in accordance with ASME or equivalent standards.
Types of Hyperbaric Chambers
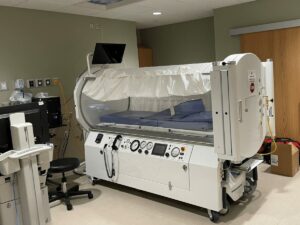
Identifying the type of chamber needed is the next vital step. At OxygenArk, our hyperbaric chambers come in two main types – monoplace and multiplace. As the names suggest, monoplace chambers are designed for a single user, while multiplace chambers can accommodate multiple users. The type of chamber significantly affects its design, the choice of materials, and the required safety features.
The table below provides a comprehensive comparison between monoplace and multiplace hyperbaric chambers, elucidating their distinct features, patient capacity, and safety considerations, assisting healthcare providers and individuals in identifying the most suitable chamber type for their specific treatment needs and facility requirements.
| Hyperbaric Chamber Type |
Description |
| Monoplace Chamber |
Designed for single-user treatment, monoplace chambers accommodate one patient at a time. These chambers are more compact and suitable for individualized therapy in private clinics or home settings. They offer ease of use and are typically transparent to reduce feelings of confinement. Safety features are tailored for single-user treatment. |
| Multiplace Chamber |
Multiplace chambers are larger and designed to accommodate multiple patients simultaneously. They are commonly used in hospitals, medical centers, and research facilities where medical staff can treat multiple patients together. These chambers have higher patient capacity and include specialized features to ensure the safety and comfort of multiple users simultaneously. |
Space and Location Requirements
The physical dimensions of the hyperbaric chamber for more flexible placement options, are largely dependent on the space available for its placement. The chosen location also influences other aspects, such as ventilation, noise control, and accessibility. Additionally, the surroundings and accessibility of the location should be taken into account to ensure the chamber fits seamlessly into its environment.

Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to the regulatory compliance standards is an essential part of constructing a hyperbaric chamber. There are numerous local, regional, and international regulations that govern the construction and operation of hyperbaric facilities. These rules cover a broad spectrum of issues, including but not limited to the types of materials, the safety features, and the qualifications required for operators.

2. Planning and Designing
After a thorough understanding of the requirements, the next stage is planning and designing the hyperbaric chamber. Here’s what to do:

Sketching the Design
Having a blueprint is instrumental for any construction project. It assists in visualizing the final product, deciding the dimensions of the chamber, the placement of the door, and the arrangement of the interior. The design should be a reflection of the purpose and space requirements identified in the previous stage. Software tools, such as AutoCAD, can be tremendously helpful in creating an accurate design.
Determining Material Requirements
The choice of construction materials hinges on the type of chamber, its intended use, and the pressure levels it is expected to withstand. Some common materials used in hyperbaric chamber construction include stainless steel, aluminium, and certain types of durable plastic. The selected materials should have high resistance to pressure, be easy to maintain, and have a long lifespan.
Safety and Comfort Considerations
User safety and comfort should always be at the forefront when planning and designing a hyperbaric chamber to maximize hyperbaric chamber benefits. This includes ensuring the chamber can safely handle the pressure levels it is designed for, providing adequate ventilation, and controlling noise levels. Comfort considerations might involve designing adjustable seating or bedding and incorporating appropriate lighting.
Involving the Right Professionals
The involvement of the right professionals in the planning and designing stage cannot be overstated. Professionals, like architects with experience in hyperbaric facilities, can provide invaluable insights into effective design strategies and potential pitfalls to avoid. They can help ensure that the design is not only functional but also compliant with all relevant regulations.
3. Acquiring Materials and Tools
Securing the right materials and tools for the project is the next crucial phase. Here’s how to effectively equip for the construction:
List of Necessary Materials
Drafting a comprehensive list of necessary materials is a critical step. This list is guided by the design plan and the choice of materials established earlier. Whether it’s stainless steel for a robust chamber shell, or high-grade silicone for airtight seals, each material requirement should be detailed and quantified accurately to prevent future shortages or excessive procurement.
Necessary Tools for the Build
Construction of a hyperbaric chamber necessitates an array of specific tools. General tools such as hammers, screwdrivers, and wrenches are fundamental. However, more specialized tools like welding equipment, pressure gauges, and precision cutting tools are equally important. It is imperative to create a comprehensive list of required tools to ensure a seamless construction process.
Safety Equipment Needed
Ensuring the team is equipped with necessary safety gear is fundamental. Protective eyewear, durable gloves, and safety helmets are just a few examples of the safety equipment needed during the construction of a hyperbaric chamber. This equipment not only protects the team but also maintains the quality of work, providing an environment where focus can be kept on precision and quality, rather than potential hazards.
4. Building the Structure of the Chamber
Once all the necessary materials, tools, and safety equipment are acquired, the exciting phase of construction begins. Let’s delve into the process:
Creating the Shell
The shell or the main body of the chamber is the first part to be constructed. This involves cutting and shaping the chosen materials based on the design sketch and then meticulously welding the pieces together. At OxygenArk, our team ensures the shell is perfectly airtight, as even a small leak can significantly affect the chamber’s functionality.
Installing the Door
The door of the hyperbaric chamber is not just an access point but a critical component that ensures the chamber’s seal and pressure integrity. The door should be designed and installed to withstand the same pressure levels as the chamber shell. This involves using robust materials for the door and installing a reliable sealing mechanism to provide an airtight closure.
Ensuring Airtight Seals
A hyperbaric chamber’s efficiency is primarily contingent on its airtight seals. Every potential leakage point, including doors, windows, and any other fixtures, should be sealed effectively to prevent any pressure loss. Using high-quality sealants and carefully inspecting each seal is mandatory to ensure optimal performance. Remember, even a minor leak can drastically affect the chamber’s functionality and safety.
5. Installing the Pressurization System
The pressurization system is the heart of a hyperbaric chamber. Here’s how to set it up:
Choosing the Right Pressure System
The pressure system choice is largely influenced by the chamber’s purpose. For instance, a medical hyperbaric chamber may require a pure oxygen system, whereas a chamber designed for diving training might use a compressed air system. The selected system must be reliable, able to generate the necessary pressure levels, and be easily controllable.
Installing the Pressure Source
Following the selection of a suitable pressure system, installing the pressure source is the next step. This usually involves setting up tanks or compressors that provide the gas used to pressurize the chamber. These sources need to be installed securely and connected to the chamber with durable, leak-proof conduits.
Connecting the Pressure System to the Chamber
Connecting the pressure system to the chamber involves setting up the channels that carry the pressurizing gas from the source to the chamber. This requires the use of high-pressure resistant hoses or pipes that are thoroughly checked for any leaks. Once the system is connected, it should be calibrated to the required pressure levels to ensure it functions as intended.
6. Installing Safety Measures
Safety measures are non-negotiable in hyperbaric chamber construction. They are instrumental in ensuring the safety of the chamber users. Here are the key safety aspects to focus on:

Emergency Release System
In any pressurized environment, an emergency release system is critical. It allows for a quick release of the internal pressure in case of an emergency. Thus, while designing and installing this system, reliability should be the topmost priority. The system should be easily accessible, simple to operate, and effective in rapidly reducing the chamber’s internal pressure.
Pressure Gauges and Control
Pressure gauges are essential to monitor the internal pressure levels of the chamber. They need to be accurately calibrated and installed in a location that is easily visible to the operator. Along with pressure gauges, an effective pressure control system is equally important. This allows for adjusting the chamber’s internal pressure as needed, providing both functionality and safety.
Ventilation and Temperature Control
According to PubMed, the construction of ventilating system, cooling device, carbon dioxide remover, automatic oxygen analyzer, and filling and maintenance devices is given. Ventilation systems must be designed to maintain fresh air supply even when the chamber is pressurized. Similarly, a temperature control system is crucial to prevent the chamber from becoming too warm due to the heat generated by pressurization.
7. Interior Fittings and Comfort
Once safety measures are in place, we shift our focus to the interior fittings and overall user comfort. Here’s what needs to be taken into account:

Installing Seating or Bedding
Whether a hyperbaric chamber is designed for short sessions or longer periods of occupancy, comfort is a must. In some medical applications, patients may need to remain in the chamber for extended periods, thus necessitating the installation of comfortable seating or bedding for convenient treatments. These installations should be secure, comfortable, and made from materials that can withstand the chamber’s environment without degrading.
Lighting Considerations
Lighting plays a crucial role in creating a comfortable and secure environment within the hyperbaric chamber. For instance, the lighting should be sufficient for users to read or carry out other activities without strain. Moreover, the lights should be designed and installed in a way that doesn’t create a risk of electric short circuiting or overheating within the chamber. Remember, safety should not be compromised for comfort.
Noise Control
Due to the enclosed nature of hyperbaric chambers, noise can be amplified and become a comfort issue. Sound-proofing or noise control materials can be integrated into the chamber’s interior to minimize noise from the pressurization system or other sources. Besides, the pressurization and ventilation systems should be designed and installed to operate as quietly as possible to ensure a comfortable user experience.
8. Testing and Calibration
Once the chamber is constructed and fitted, testing and calibration become the center of attention. Here are the essential steps:
Initial Testing
Initial testing involves checking the hyperbaric chamber’s structural integrity and ensuring that all the systems function as intended. This includes testing the pressurization system for leaks, validating the safety measures like the emergency release system, and confirming that the interior fittings are secure and comfortable. Any flaws detected should be corrected immediately to ensure that the chamber meets the required standards.
Fine-Tuning and Calibration
After initial testing, fine-tuning, and calibration of the pressure system and safety controls come next. The pressure system should be calibrated to accurately reflect and control the chamber’s internal pressure. Similarly, safety controls, like the emergency release system and pressure gauges, should be tested and calibrated for accuracy and reliability.
9. Final Assembly and Safety Check
The last phase is to complete any final assembly and conduct a comprehensive safety check. Here’s what this entails:
Final Assembly
Any remaining parts or systems that were not installed during the main construction are fitted at this stage. This may include finalizing the interior fittings, installing the external controls, and setting up the power supply. It’s important to follow the design plan accurately and ensure that all components are securely installed.
Safety Check
Finally, a comprehensive safety check is conducted. This includes a final test of all safety measures, a thorough inspection of the chamber for any possible leaks, and a check of all controls and systems to ensure they are functioning properly. It’s crucial to take time over this step, as any oversights can lead to safety issues down the line.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.
Conclusion
It’s essential to highlight that constructing a safe and efficient hyperbaric chamber is a complex process, requiring a careful approach and attention to detail at every stage. However, with a systematic approach guided by the steps laid out above, it’s a task that can be successfully accomplished.
Remember, if this process seems daunting, professional assistance is always an option. OxygenArk, a renowned manufacturer of hyperbaric chambers, is a trusted name in the industry and is always ready to lend its expertise. Don’t hesitate to reach out and explore the comprehensive solutions OxygenArk offers in the world of hyperbaric chambers. To learn more or discuss specific needs, don’t hesitate to contact them.






