Are you leveraging the optimal oxygen levels for your healthcare services? Effective oxygen management can drastically improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency in medical settings.
With years of experience in hyperbaric technologies and a deep understanding of medical oxygen’s impact, I’m here to share valuable insights that can transform patient care in your facility.
The importance of medical oxygen percentage cannot be overstated. Precise oxygen levels are essential for therapeutic efficacy, safety, and patient recovery in numerous medical applications.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the importance of medical oxygen percentage, explore its effects on patient health, and understand how to leverage oxygen effectively.
Read on for a detailed exploration!
1. Defining Medical Oxygen Percentage
Medical oxygen percentage refers to the concentration of oxygen that is delivered to patients during treatment. This measurement is critical in healthcare settings to ensure the oxygen supplied meets the precise needs of each patient. It’s a foundational aspect of respiratory therapies and critical care.
Understanding the exact percentage of oxygen in a medical context is vital. It helps healthcare professionals adjust the oxygen flow to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. This adjustment is crucial for patient safety and effective treatment outcomes across various medical conditions. Trust me, getting this right can make all the difference.

2. The Importance of Proper Oxygen Levels
After defining medical oxygen percentage, it’s crucial to understand why maintaining the right oxygen levels is so important. Here are key points highlighting this significance:
- Optimizes Healing and Recovery: I’ve always emphasized that adequate oxygen levels are crucial for the body’s healing process. Proper oxygenation lets tissues receive the oxygen necessary for repair, making it especially important in medical recovery.
- Enhances Athletic Performance: For athletes, optimal oxygen levels can enhance performance and endurance. By ensuring tissues are well-oxygenated, athletes can maximize their energy and recovery rates during and after physical activity.
- Supports Cognitive Functions: Adequate oxygen levels are essential for brain health, impacting cognitive functions such as memory, focus, and problem-solving. Proper oxygenation contributes to mental clarity and overall brain function.
- Prevents Hypoxemia: Hypoxemia is a condition where blood oxygen levels are below normal and can lead to severe health issues. Proper oxygen levels help prevent this condition and its dangerous complications, such as organ damage.
- Alleviate Chronic Conditions: Patients with chronic respiratory conditions like COPD or asthma can have an improved quality of life with proper oxygen therapy. This approach helps manage symptoms and reduces the frequency of acute exacerbations.

3. Optimal Oxygen Levels for Different Conditions
Understanding the importance of proper oxygen levels brings us to how these levels vary across different medical conditions. Here are key conditions and their optimal oxygen requirements:
Chronic COPD
Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) require carefully managed oxygen therapy. An optimal target is to maintain oxygen saturation (SpO2) between 88% to 92%. This range helps in preventing hypoxia without risking oxygen toxicity, which is a concern in COPD management.
Acute Asthma
During an asthma attack, maintaining oxygen saturation above 94% is crucial for patient safety. It helps guarantee that enough oxygen reaches the lungs, which are struggling to function correctly. This level supports the body during the increased demand for oxygen caused by restricted airways.
Heart Failure
For individuals experiencing heart failure, oxygen therapy aims to keep SpO2 levels at or above 90%. This threshold supports heart function by ensuring that the muscles receive enough oxygen to work efficiently, especially during periods of stress or activity. Seeing patients regain their strength is incredibly rewarding.
Sleep Apnea
In sleep apnea, the goal is to prevent drops in oxygen levels during sleep. Optimal oxygen supplementation can help maintain a saturation level that prevents the dangerous lows that can occur with this condition. Continuous or bilevel-positive airway pressure machines are often used to achieve this. It’s amazing how much a good night’s sleep can improve someone’s life.

4. Clinical Applications of Medical Oxygen
Building on our understanding of optimal oxygen levels for various conditions, let’s explore how medical oxygen is applied clinically to treat these and other health challenges. Here are some primary applications:
Emergency Care
In emergencies, rapid oxygenation is vital to stabilize patients. Medical oxygen is administered to improve oxygen saturation levels in the blood, supporting vital organ function. It’s especially crucial for heart attack, stroke, or trauma victims, ensuring tissues receive enough oxygen to minimize damage. The use of Oxygen-ark’s chambers in these scenarios guarantees prompt and effective oxygen delivery.
Surgical Support
During surgery, maintaining patient oxygenation is essential. Medical oxygen guarantees that patients’ oxygen levels remain stable while under anesthesia, reducing the risk of hypoxia and supporting organ function. It’s a standard procedure to prevent complications and aid in a smoother recovery process. Ensuring a patient wakes up safely from surgery is one of the most crucial parts of the process.
Chronic Management
For those with chronic respiratory conditions, long-term oxygen therapy can significantly improve lifespan and activity levels. It helps in managing symptoms, decreasing hospitalization rates, and improving overall well-being. Continuous or intermittent oxygen therapy is adjusted based on the patient’s oxygen saturation levels and lifestyle needs.
Neonatal Care
In neonatal units, precise oxygen delivery is critical for premature infants with underdeveloped lungs. Medical oxygen, administered in controlled concentrations, supports lung development and prevents hypoxemia. Careful monitoring is necessary to avoid oxygen toxicity, balancing the need for oxygenation with the risk of retinopathy of prematurity and other complications.

5. The Process of Adjusting Oxygen Levels for Patients
Following the exploration of medical oxygen’s clinical applications, it’s essential to understand how healthcare professionals adjust oxygen levels for individual patient needs. Here are the steps involved in this critical process:
Step#1 Measure Oxygen
First, a small device, often placed on the finger, measures the patient’s current oxygen level. This reading tells medical staff if the patient needs more oxygen. It’s quick and doesn’t cause any pain. Based on this, they know whether to start or adjust oxygen therapy.
Step#2 Set the Goal
After measuring, doctors decide what the ideal oxygen level should be for the patient’s specific health condition. This target is based on medical guidelines and the patient’s overall health. Setting this goal helps guide the adjustment of oxygen flow, a critical step for effective treatment.
Step#3 Adjust Flow
To change oxygen levels, medical staff adjust the oxygen flow rate on the delivery system, like an oxygen concentrator or tank. They increase or decrease the flow to get the right amount of oxygen to the patient. This step requires careful attention to make sure the patient gets just what they need. The adjustment depends on the initial measurement and the set goal.
Step#4 Monitor Changes
After adjusting the oxygen, the patient’s levels are continuously monitored to see how they respond. This monitoring is done with the same type of device used initially. Here’s the interesting part, it helps verify the adjustment is effective and that the patient’s oxygen level is moving toward the target. If not, further adjustments might be needed.
Step#5 Fine-tune as Needed
Finally, the oxygen levels are fine-tuned based on continuous monitoring. If the patient’s condition changes or if they haven’t reached the targeted oxygen level, the flow rate is adjusted again. This step may be repeated several times to maintain the right oxygen level. It’s all about finding the balance for the patient’s specific needs.
6. The Impact of Incorrect Oxygen Percentage
After explaining how to adjust oxygen levels for patients, it’s important to understand the risks of not getting these adjustments right. Here’s how incorrect oxygen percentages can affect patients:
Low Oxygen Risks
When patients receive too little oxygen, they can become hypoxic, meaning their body isn’t getting enough oxygen. This can lead to symptoms like confusion, breathlessness, and a fast heart rate. Over time, chronic hypoxia can damage organs like the brain and heart. It’s critical to correct low oxygen levels quickly to avoid these serious health issues.
High Oxygen Dangers
According to Health Shots, the normal oxygen levels are considered to be between 80 and 100 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) or 95-100 percent. Too much oxygen can also be harmful, leading to a condition called oxygen toxicity. This can cause lung damage, leading to coughing and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, it can also affect the central nervous system, causing symptoms like dizziness or seizures.
Organ Damage
Incorrect oxygen levels, whether too high or too low, can lead to long-term organ damage. For example, organs like the lungs, heart, and brain rely on a precise balance of oxygen to function properly. Damage from incorrect oxygen levels can be irreversible and impact a patient’s quality of life significantly. Ensuring accurate oxygen delivery is key to preventing organ damage.
Recovery Delays
For patients recovering from surgery or illness, incorrect oxygen levels can slow down the healing process. Wounds need the right amount of oxygen to heal properly, and too little can delay this process. On the other hand, too much oxygen can cause oxidative stress, also hindering recovery. Correct oxygen levels support a faster and more effective recovery.
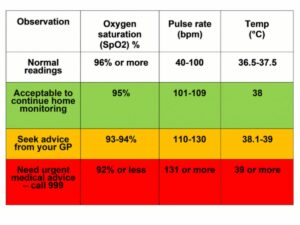
7. 4 Tips on How to Determine the Right Oxygen Percentage
Understanding the negative effects of incorrect oxygen percentages underscores the need for precision in oxygen therapy. Below are the practical tips for determining the right oxygen percentage for patients:
#1 Use Targeted SpO2 Ranges
Identify the targeted SpO2 range for the patient’s specific condition, as these ranges vary. For most adults, maintaining a SpO2 between 94% to 98% is considered ideal, but patients with chronic conditions like COPD may have lower targets, such as 88% to 92%. This approach ensures you’re aiming for a specific, condition-appropriate oxygen saturation level.
#2 Utilize a Pulse Oximeter
A pulse oximeter, a small device that clips onto a patient’s finger, is a tool I frequently rely on to measure their blood oxygen level. It gives a quick and painless reading of how much oxygen is in the blood, shown as a percentage. Aim for a reading that matches the target oxygen saturation for the patient’s condition, which is often between 94% to 98%.
#3 Inspect Respiratory Rate
Observing a patient’s respiratory rate which is the number of breaths they take per minute can also help in adjusting oxygen levels. For instance, a normal respiratory rate for adults is typically between 12 to 20 breaths per minute. If the rate is too high or too low, it might indicate that the current oxygen percentage is not optimal for the patient.
#4 Use Advanced Equipment
Utilize advanced oxygen delivery systems, like those offered by Oxygen-ark, which allow for precise adjustments in oxygen levels. These systems can make it easier to set and maintain the correct oxygen percentage. Some equipment also provides monitoring features, offering real-time feedback on patient response. Investing in quality equipment supports better treatment outcomes.
This table provides a simplified overview of how to adjust the oxygen percentage based on respiratory rate and observed patient condition:
| Respiratory Rate (breaths/min) |
Condition |
Recommended Oxygen % |
| <12 |
Hypoventilation |
High (e.g., 40-60%) |
| 20-Dec |
Normal |
21% (Room Air) |
| 21-28 |
Mild Distress |
Increased (e.g., 25-35%) |
| >28 |
Severe Distress |
Very High (e.g., 60-100%) |
| Varies |
Depends on Patient |
Customized |
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.
Conclusion
Understanding the precise role of medical oxygen percentage in healthcare is key to improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. This guide has highlighted the importance of accurate oxygen levels across various medical scenarios.
For businesses seeking in-depth insights and solutions related to medical oxygen percentage, Oxygen-ark offers expert guidance and products fitted to your needs. To explore how we can assist you, please contact us.





