Can advanced oxygen therapy transform the standard of care in diverse professional settings? Absolutely, by integrating precise oxygen inhalation procedures, this transformation is within reach.
With extensive experience in hyperbaric technologies, our insights into oxygen therapy are grounded in both practice and science.
Oxygen inhalation is more than a medical procedure; it’s a gateway to enhanced recovery and performance. Its significance spans various fields, reflecting its adaptability and effectiveness.
In this guide we will walk you through the oxygen inhalation procedure, covering key steps and considerations to ensure efficacy and safety.
Discover the integration of this method into your practice!
Step#1 Preparation for Oxygen Inhalation
Initiating the oxygen inhalation process is crucial for ensuring both its effectiveness and safety. Here’s why that’s important: a well-prepared setup is the foundation of a successful outcome.
- Ensure the Environment is Safe: The initial step is to make sure the environment is secure and conducive to the procedure. Safety first not only sets the stage for a smooth operation but also instills confidence in the team.
- Gather Necessary Equipment: Collect all the required equipment, including the oxygen delivery system, masks or nasal cannulas, and monitoring devices. Having everything at hand streamlines the process, which is amazing, isn’t it? It saves time and reduces the stress of searching for items last minute.
- Check the Oxygen Supply: Inspecting the oxygen tank or concentrator to confirm it’s in working order and filled with oxygen is critical. This step guarantees the procedure can proceed uninterrupted, providing peace of mind to all involved.
- Review the Patient’s Information: It’s vital to be familiar with the patient’s medical history, current health status, and specific oxygen requirements. Customizing the oxygen therapy to meet the patient’s needs, highlights the facility’s commitment to personalized care.

Step#2 Selecting the Correct Oxygen Delivery System
After setting up the environment and gathering tools, selecting the right oxygen delivery system is crucial, especially with the oxygen therapy market expected to grow to USD 60.08 billion by 2032, according to Precedence Research. Let’s dive into this key selection process:
- Understand Patient Needs: Start by assessing the patient’s specific oxygen requirements, considering their medical condition and oxygen saturation levels. Anyone will agree that this initial evaluation is crucial, as it directly influences therapy’s success.
- Consider the Oxygen Concentration Required: Different systems deliver varying levels of oxygen. For instance, nasal cannulas are fit for lower oxygen demands, whereas masks can provide higher concentrations.
- Evaluate the Patient’s Comfort and Mobility: Some patients may favor a less intrusive option like a nasal cannula for its comfort and ease of mobility, especially if long-term oxygen therapy is needed.
- Review Equipment Compatibility: Confirm that the chosen delivery system is compatible with your existing oxygen supply equipment. This step prevents unforeseen issues and guarantees a seamless integration into the patient’s care regimen.

Step#3 Setting Up the Oxygen Equipment
Having selected the correct oxygen delivery system, the focus shifts to setting up the equipment properly. Here are the steps to ensure a smooth and efficient setup process:
- Inspect the Equipment: Before anything else, thoroughly inspect the oxygen delivery system for any damage or malfunction. This initial check is essential to guarantee the equipment’s reliability during use.
- Connect the Oxygen Source: Attach the oxygen delivery system to the oxygen source, whether it’s a tank or a concentrator. Ensure the connection is secure to prevent any leaks.
- Adjust the Oxygen Flow Rate: Based on the patient’s prescription, set the oxygen flow rate on the delivery system. Accurate flow rate adjustment is critical for meeting the patient’s oxygenation needs.
- Position the Delivery Device Comfortably: Whether using a mask or a nasal cannula, position it comfortably on the patient’s face. Comfort is key to patient compliance, especially for those requiring extended oxygen therapy.
- Perform a Final Check: Before starting the oxygen therapy, perform a final check of the equipment and settings. Confirm that the flow rate is as prescribed and that the patient is comfortable with the delivery device’s fit.

Step#4 Administering Oxygen
With the oxygen equipment set up and double-checked, the next phase is the actual administration of oxygen to the patient. Here are the critical actions to take during oxygen administration:
- Start the Oxygen Flow: Begin by initiating the flow of oxygen according to the prescribed rate. As a matter of fact, it’s essential to monitor the system closely as you start to ensure the oxygen is flowing correctly.
- Observe the Patient’s Response: OxygenArk suggests to observe the patient closely for any immediate reactions to the oxygen therapy, such as difficulty breathing or discomfort.
- Adjust as Needed: If the patient shows signs of discomfort or if their oxygen saturation levels indicate a need, adjust the flow rate or the position of the delivery device.
- Communicate with the Patient: Keep the lines of communication open with the patient throughout the administration process. Encouraging them to report any discomfort or concerns enhances their sense of safety and involvement in their care.

Step#5 Monitoring the Patient
Following the administration of oxygen, continuous monitoring of the patient becomes the linchpin in the therapy’s success. Here are essential steps to ensure ongoing patient safety and therapy efficacy:
- Regularly Check Oxygen Saturation Levels: Use a pulse oximeter to frequently monitor the patient’s oxygen saturation. This allows for real-time assessment of how well the patient is responding to the therapy.
- Observe for Any Signs of Discomfort or Adverse Reactions: Watch for any signs of discomfort, for instance, skin irritation from the delivery device, or signs of oxygen toxicity. Prompt identification and action can mitigate potential issues, maintaining the patient’s comfort and safety.
- Document the Therapy Progress: Keep detailed records of the patient’s response to the therapy, including oxygen saturation levels, any adjustments made to the flow rate, and any feedback from the patient. Remember that accurate documentation supports ongoing patient care and future therapy planning.
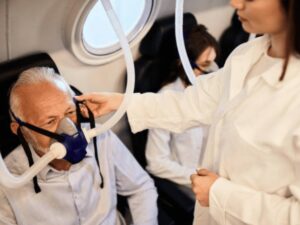
Step#6 Adjusting Oxygen Flow
Continuous monitoring leads naturally to the potential need for adjusting the oxygen flow, a critical step in tailoring the therapy to the patient’s evolving needs. Here’s how to effectively adjust oxygen flow:
- Assess Need Based on Saturation Levels: Regularly checking the patient’s oxygen saturation levels will indicate whether an adjustment in the oxygen flow is necessary. If levels are outside the target range, an adjustment may be required to either increase or decrease the oxygen flow.
- Consult the Prescribing Physician: Before making any adjustments, consult with the physician who prescribed the oxygen therapy. Similarly, they can provide guidance on the appropriate adjustments based on the patient’s condition and therapy goals.
- Make Incremental Adjustments: When adjusting the oxygen flow, do so in small increments to avoid abrupt changes that could negatively affect the patient. This cautious approach ensures the patient’s safety and comfort while allowing for precise control over their oxygenation.
- Check Patient Response: After adjusting the oxygen flow, closely monitor the patient’s response to ensure the adjustment is beneficial. Pay attention to their oxygen saturation levels, as well as any subjective feedback regarding comfort and breathing ease.

Step#7 Safety Measures and Precautions
Following adjustments to the oxygen flow, it’s imperative to underscore the importance of safety measures and precautions. This ensures the therapy remains beneficial without introducing risks.
- Regular Equipment Checks: Routinely inspect oxygen delivery systems for any signs of wear or damage. Ensuring equipment is in optimal condition is key to preventing leaks or malfunctions that could compromise the therapy’s safety.
- Avoid Flammable Materials: Keep flammable materials away from the oxygen delivery area. Oxygen supports combustion, and its presence increases the fire risk.
- Educate Staff and Patients: Ensure that all staff and, when applicable, patients are informed about the oxygen therapy’s potential risks and safety protocols. Knowledge empowers individuals to act swiftly and appropriately in preventing incidents or responding to emergencies.
- Emergency Preparedness: Have a clear plan in place for responding to oxygen-related emergencies. At OxygenArk, this includes knowing how to quickly shut off the oxygen supply and having fire extinguishers readily available.
Here’s a simple table outlining the key safety measures and precautions for the oxygen inhalation procedure:
| Measure |
Description |
Why It’s Important |
| Verify Oxygen Purity |
Ensure the oxygen supply is medical-grade and free from contamination. |
To prevent complications associated with inhaling impure or contaminated oxygen. |
| Check Oxygen Equipment |
Inspect the oxygen tank, regulator, and delivery system for damage. |
To ensure the equipment is in good working condition and prevent leaks or malfunctions. |
| Monitor Oxygen Flow Rate |
Adjust the flow rate as prescribed by a healthcare professional. |
To provide the appropriate amount of oxygen, avoiding the risks of too much or too little oxygen. |
| Avoid Open Flames and Heat |
Keep away from open flames, cigarettes, and electrical devices that can spark. |
Oxygen supports combustion; exposure to flames or heat can result in fires or explosions. |
| Use in a Well-Ventilated Area |
Ensure the area is well-ventilated to avoid oxygen accumulation. |
To prevent the risk of oxygen toxicity from high concentrations and ensure the safety of the environment. |
Step#8 Post-Procedure Care
After implementing safety measures and concluding the oxygen therapy session, post-procedure care becomes the next focus to ensure patient well-being and therapy effectiveness. Here’s how to approach this vital phase:
- Assess the Patient’s Condition: Immediately following the session, evaluate the patient’s response to the therapy, including checking oxygen saturation levels and overall comfort.
- Provide Patient Instructions: Offer clear instructions for the patient or their caregivers on any follow-up care or observations necessary after the session. Highlighting signs of potential complications and when to seek further medical advice empowers patients in their recovery process.
- Schedule Follow-up Appointments: Arrange for follow-up appointments to monitor the patient’s progress and make any necessary adjustments to their treatment plan.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing an oxygen inhalation procedure effectively can mark a significant upgrade in patient care and outcomes. This guide aims to equip you with a detailed walkthrough of the process, emphasizing the importance of precision, and safety across different settings and applications.
For those looking to integrate state-of-the-art oxygen therapy solutions into their operations, OxygenArk offers the tools and support to elevate your care offerings. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help.






