Ever pondered on the vital role oxygen plays in the health sector? It’s an everywhere element, yet its lack could endanger the operations of countless medical establishments. Indeed, a decrease in oxygen concentration can lead to severe complications, presenting a considerable problem for both patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Enter Oxygen Therapy – a solution designed to tackle this issue head-on. It is a medical treatment aimed at improving a patient’s oxygenation status through the administration of supplemental oxygen. Particularly helpful for those with breathing disorders. In this comprehensive guide, the intricacies of this therapy will be explained, from its various applications.
Stay tuned and read on!
1. Understanding How Oxygen Therapy Works
Dive into the intriguing world of oxygen therapy, a marvel of medical science that’s rewriting the rulebook of healthcare. This topic unravels the ingenious mechanisms behind the delivery of oxygen to the body and how it impacts cellular metabolism. Here is a brief overview to know more:
Oxygen Delivery Mechanism
Oxygen therapy primarily operates by supplying supplemental oxygen to patients struggling with low oxygen levels in their blood. It’s delivered via devices like nasal prongs or masks. As I have been in this industry, I’ve seen firsthand how this mechanism can drastically improve patients’ conditions. Additionally, these oxygen-rich air particles then journey into the lungs where the actual gas exchange occurs.
The Role of Hemoglobin in Oxygen Distribution
Hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein in red blood cells, plays a significant role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. Acting as a taxi for oxygen, hemoglobin can carry up to four oxygen molecules at a time. The binding and unbinding of oxygen molecules to hemoglobin is a dynamic process that ensures every corner of the body gets its fair share of oxygen.
Oxygen Therapy and Cell Metabolism
A key aspect of oxygen therapy lies in its ability to stimulate cell metabolism. It does so by supplying extra oxygen to cells, which then utilize it in the process of breaking down food for energy production. This metabolic boost can have an overwhelmingly positive impact on the body’s overall health and functionality.
2. Benefits of Oxygen Therapy
The wonders of oxygen therapy extend far beyond its medical applications. It serves as a catalyst for improved tissue oxygenation, a boon for physical endurance, and a potent tool for enhancing sleep quality. Here are some important details to keep in mind:
Improving Tissue Oxygenation
Among the key benefits of oxygen therapy is its ability to improve tissue oxygenation. By delivering an enhanced amount of oxygen, it ensures tissues get their required oxygen levels to function optimally. This increased oxygenation can accelerate wound healing and reduce the risk of tissue damage.
Enhancing Physical Endurance
Oxygen therapy can also play a critical role in enhancing physical endurance. By supplying additional oxygen, it helps muscles to produce more energy during physical activities. Based on experience, the physical improvements I’ve witnessed in patients using oxygen therapy are truly remarkable. Over time, this can translate to increased strength, endurance, and overall physical performance.
Aiding in Sleep Quality
A key application of oxygen therapy is found in the treatment of sleep disorders like sleep apnea. By maintaining optimum oxygen levels throughout the night, it prevents the occurrence of low oxygen episodes that could potentially disrupt sleep. For example, OxygenArk, a renowned hyperbaric chamber manufacturer, offers devices that can ensure an uninterrupted oxygen supply, thereby enhancing sleep quality.
3. Different Types of Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. With the varying needs of patients and diverse healthcare scenarios, it manifests in different forms. The therapies range from low and high flow to hyperbaric oxygen therapy, each catering to distinct medical conditions. It’s essential to remember the following:
Low Flow Oxygen Therapy
Low flow oxygen therapy, as the name suggests, supplies a lower amount of oxygen, typically less than the patient’s minute ventilation. Among the commonly used devices for this therapy include the nasal cannula and the simple mask. Both are ideal for stable patients whose oxygen requirements are relatively moderate.
A nasal cannula consists of a lightweight tube that splits into two prongs placed in the nostrils. It provides an oxygen concentration of 24-44%, dependent on the flow rate. In my experience, patients generally find it comfortable and less intrusive. It’s simple, cost-effective, and suitable for long-term oxygen therapy.
A simple mask covers the nose and mouth and delivers a higher oxygen concentration than a nasal cannula. Typically used in acute settings, it offers an oxygen concentration of 35-50% and is a preferred choice in emergencies due to its ease of application and immediate effects.
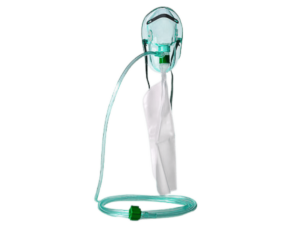
High Flow Oxygen Therapy
High flow oxygen therapy delivers a greater volume of oxygen, matching or exceeding a patient’s inspiratory flow demand. The popular devices here are the Venturi mask and the non-rebreather mask. These are designed to offer more accurate and higher concentrations of oxygen, especially beneficial in acute care scenarios.
A Venturi mask employs a method to deliver precise levels of oxygen. It’s designed with a mechanism that mixes a high-flow rate of oxygen with room air. This ensures a constant, fixed concentration of inspired oxygen, making it a preferred choice in critical care where tight control over oxygen levels is necessary.
A non-rebreather mask provides the highest concentration of oxygen among low-flow systems, reaching up to 90-100%. It features a reservoir bag that fills with pure oxygen, delivered to the patient upon inhalation. Ideal for short-term therapy, it is often used in acute situations requiring high oxygen concentrations.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves the use of a special chamber where the patient breathes in 100% oxygen under pressure higher than sea level. This allows a greater amount of oxygen to be dissolved in the bloodstream, thus reaching tissues more efficiently. Having been part of numerous hyperbaric sessions, I can attest to the dramatic health improvements it can foster.
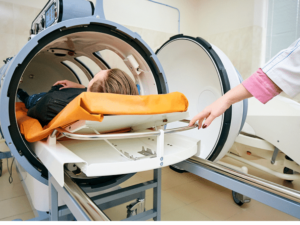
4. Equipment Used in Oxygen Therapy
The efficiency of oxygen therapy is greatly influenced by the quality and appropriateness of the equipment used. This section sheds light on the common devices in oxygen therapy. Here are some to explore:
Oxygen Concentrators
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices that filter room air to produce concentrated oxygen for therapeutic use. They operate by separating oxygen from other gases, resulting in a constant supply of high-concentration oxygen. Compact, portable, and cost-effective, they are becoming an increasingly popular choice for oxygen therapy.

Oxygen Tanks
Oxygen tanks store medical-grade oxygen in gaseous form under pressure. When released, the gas expands, providing a steady flow of oxygen through a regulator that controls the flow rate. Despite their size and weight, they remain a reliable source of high-concentration oxygen, especially in stationary settings.

Oxygen Masks and Nasal Cannulas
Oxygen masks cover the nose and mouth, allowing the delivery of higher concentrations of oxygen. Nasal cannulas, on the other hand, are tubes with two prongs inserted into the nostrils, providing a more comfortable option for long-term use. The selection between a mask and a cannula largely depends on the patient’s condition and oxygen requirement.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers
Hyperbaric chambers are specially designed devices for administering hyperbaric oxygen therapy. They are built to withstand high pressures and can accommodate one or multiple patients. When considering a purchase options, healthcare facilities might want to explore offerings from OxygenArk, known for their robust and advanced hyperbaric chambers. Check it out now!
5. Medical Conditions That Benefit from Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy stands as a beacon of hope for patients grappling with respiratory diseases, enabling them to lead a better quality of life. This therapy has been instrumental in managing several medical conditions, alleviating the symptoms, and enhancing overall health. Let’s delve into some of the illnesses where oxygen therapy plays a crucial role.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD involves conditions that obstruct airflow and lead to breathing difficulties. According to CDC, COPD makes breathing difficult for the 16 million Americans who have this disease. Oxygen therapy serves as a lifeline for these patients, compensating for the lack of oxygen absorbed by their lungs.
Asthma
Asthma patients can experience severe attacks where the air passages in their lungs narrow down, reducing oxygen intake. Oxygen therapy can provide relief during these episodes, ensuring that their bodies receive the vital oxygen required for functioning. In this context, I’d like to stress that immediate medical attention and appropriate therapy can significantly help manage the condition effectively.

Pneumonia
A lung infection that can affect one or both lungs, often results in difficulty breathing due to inflammation and fluid-filled air sacs is Pneumonia. Oxygen therapy can supplement the decreased levels of oxygen, helping to stabilize the patient and speed up recovery.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a disorder that interrupts breathing during sleep, causing reduced oxygen supply to the brain and the rest of the body. Oxygen therapy has been found effective in ensuring a continuous oxygen supply, thus mitigating the risks associated with the condition.

Cystic Fibrosis
A genetic disorder, results in the formation of thick, sticky mucus in the lungs, hindering normal respiratory functions – Cystic Fibrosis. Oxygen therapy is often recommended to overcome the oxygen deficit and maintain normal oxygen levels in the body. It’s noteworthy how beneficial this therapy can be in the management of this condition.
Heart Failure
Heart failure, characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently, can result in the body not receiving enough oxygen. Oxygen therapy, in such cases, can aid in providing the necessary oxygen supply, supporting the heart function and improving patients’ overall health.
Covid-19
With Covid-19, patients may experience severe respiratory problems, leading to lower oxygen levels. The strategic use of oxygen therapy has been a critical aspect of managing severe Covid-19 cases, ensuring that patients’ oxygen levels remain stable during the illness
6. The Process of Administering Oxygen Therapy
Administering oxygen therapy necessitates a comprehensive and meticulous approach, ensuring its efficacy in managing various health conditions. The process involves several steps, each crucial for the effective implementation of therapy. Make a mental note of these key points:
Step#1 Diagnosis and Assessment
Before starting oxygen therapy, healthcare providers conduct a thorough diagnosis and assessment of the patient’s condition. This involves testing the amount of oxygen in their arterial blood, which can be done using a pulse oximeter. Low levels indicate that a person may benefit from supplemental oxygen.
Step#2 Determining the Right Oxygen Concentration
Post diagnosis, healthcare providers decide the appropriate oxygen concentration necessary for the patient. This decision takes into account various factors such as the specific medical condition, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s overall health status.
Step#3 Modes of Delivery
There are different types of devices for oxygen therapy, such as nasal cannulas or face masks. For patients requiring higher concentrations of oxygen, healthcare providers might recommend a hyperbaric chamber, which delivers 100% oxygen at a pressure higher than normal air pressure. Look for companies that manufacture hyperbaric chambers, which can be considered a viable option for oxygen therapy.
Step#4 Monitoring and Adjustment
Once therapy commences, healthcare providers monitor the patient’s condition and response to therapy. Based on my observations, they may adjust the oxygen levels, ensuring optimal health outcomes for the patient. The monitoring process serves as a cornerstone for oxygen therapy, guiding its administration and effectiveness.
7. The Cost and Accessibility of Oxygen Therapy
While oxygen therapy cost can vary widely depending on the specifics of the treatment plan, the average expense typically ranges between $200 to $800 per month, factoring in the equipment, maintenance, and operational costs. Insurance coverage can, however, mitigate these costs, though the extent of coverage may depend on the provider and the specific policy.
As the global healthcare industry recognises the necessity of oxygen therapy, efforts are underway to make it more affordable and accessible. I believe, the accessibility of oxygen therapy, on the other hand, depends on numerous factors, including geographical location, healthcare infrastructure, and more.
| Aspect |
Oxygen Therapy |
| Cost |
Can be Expensive, Insurance Coverage may help. |
| Accessibility |
Widely Accessible in hospitals, clinics, and homecare settings. |
| Portability |
Varies Depending on Equipment, Portable options available. |
| Home Oxygen Therapy |
Common for Chronic Conditions, Improves quality of life. |
| Traveling with Oxygen |
Requires Planning, Portable options for travel available. |
8. Risks and Side Effects of Oxygen Therapy
Like all medical interventions, oxygen therapy is not without its risks and side effects. While it is largely beneficial, understanding the potential complications associated with it can help healthcare providers make informed decisions and manage patient expectations. Balancing the benefits with the potential risks is an integral part of patient-centered care. Take these important details into consideration:
Oxygen Toxicity
Oxygen toxicity, a potential side effect of prolonged or excessive oxygen therapy, results from an overload of oxygen in the body tissues. Symptoms can range from mild, such as chest pain or shortness of breath, to severe cases involving seizures or respiratory failure. Though rare, it is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor oxygen levels and adjust the treatment plan as necessary to prevent this condition.
Dry or Bloody Nose
Another common side effect of oxygen therapy is a dry or bloody nose. This is often a result of the drying effect that the oxygen has on the nasal passages. I remember one of patient complaining of constant nosebleeds and discomfort due to this. Interventions like using a humidifier with the oxygen device or applying a water-based lubricant can help alleviate these symptoms.
Skin Irritation
Oxygen therapy can also cause skin irritation, particularly around the area where the oxygen is delivered, such as the face or the nose. This is often due to the continuous contact of the oxygen mask or cannula with the skin. In my experience, patients often find this to be one of the most uncomfortable side effects, but it can be managed with good skincare routines and regular equipment cleaning.
Risks of Fire
Finally, the risk of fire is an important consideration with oxygen therapy. Oxygen supports combustion, and as such, improper handling can lead to fires. For example, there have been instances where fires have started due to smoking near oxygen equipment. Strict safety guidelines, like keeping oxygen equipment away from open flames and not smoking near the device, can help mitigate this risk.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.
Conclusion
Wrapping up our exploration of Oxygen Therapy, a multifaceted treatment addressing issues of accelerated wound healing and wellness it’s clear that this modality plays a pivotal role in many healthcare scenarios. Considering the essential role Oxygen Therapy plays in the healthcare landscape, how is your business staying updated on the latest advancements?
Hyperbaric chambers, like those manufactured by OxygenArk, are particularly instrumental in delivering therapy, enabling high oxygen concentrations and potentially enhancing our body’s healing capabilities. To address queries and discussions, insights, or collaborations, don’t hesitate to reach out. Let’s collectively enhance patient care with leading-edge oxygen therapy solutions. Contact us now!














